Antennas, Antenna Cables, Wireless Products: Technical Articles
UV Resistance in Antenna Cables: Which Coax Types Are Suitable?
Listen to article
Audio generated by DropInBlog's Blog Voice AI™ may have slight pronunciation nuances. Learn more
UV Resistance in Antenna Cables
UV resistance is essential when selecting a coaxial cable for outdoor antenna installations. Sunlight can degrade certain materials, causing the cable's outer jacket to crack or deteriorate, compromising signal integrity and reducing the cable's lifespan. Here’s an overview of which common coaxial cable types are UV-resistant:

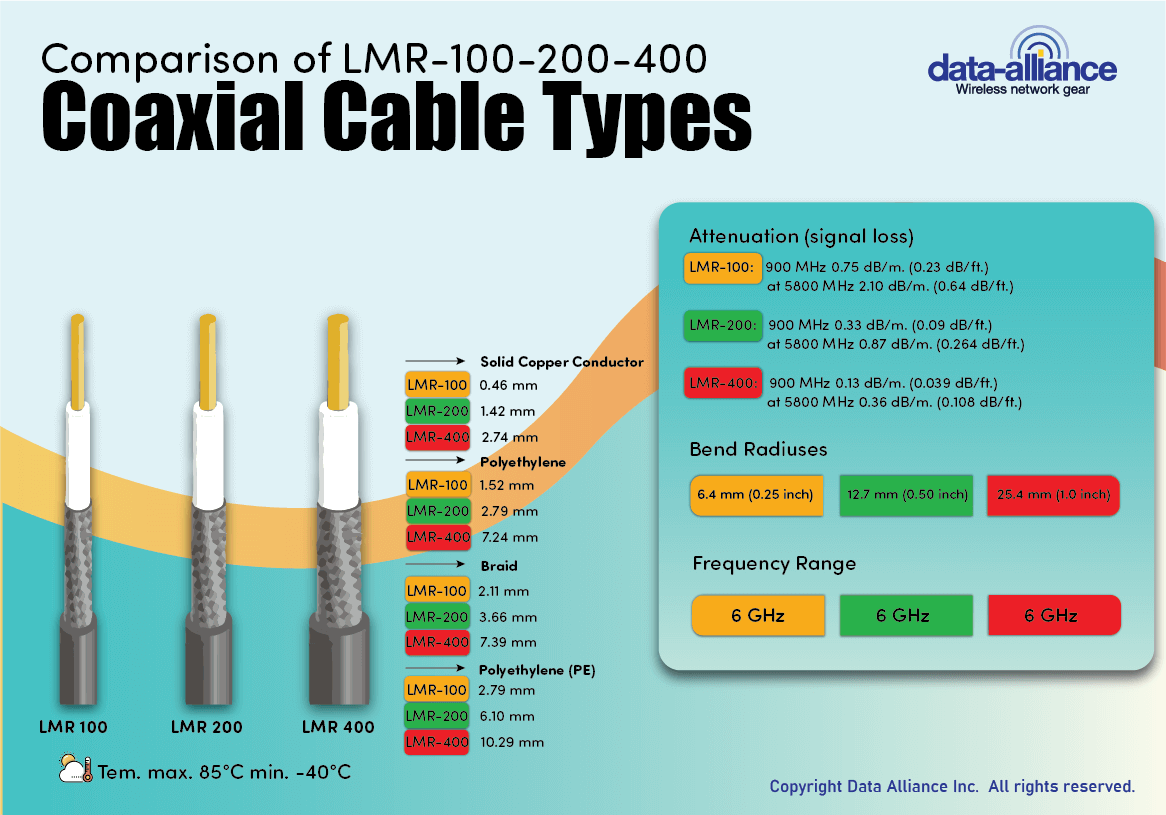
1. LMR-100, LMR-200, LMR-400
- UV Resistance: Yes
- Details: The LMR series cables, manufactured by Times Microwave Systems, are well-regarded for their durability, including UV resistance. These cables use a polyethylene (PE) outer jacket, inherently resistant to UV radiation. The LMR series (including LMR-100, LMR-200, and LMR-400) provides a good balance between flexibility and weather resistance, making them ideal for outdoor applications, such as antenna feeds, where prolonged sun exposure is expected.
2. RG-174
- UV Resistance: No (standard)
- Details: RG-174 cables typically come with a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) outer jacket, which is not inherently UV resistant. PVC can degrade when exposed to UV radiation for extended periods, causing cracks and signal leakage. RG-174 is not recommended for outdoor use unless it is explicitly labeled as having a UV-resistant jacket or installed within a protective conduit.

3. RG-178
- UV Resistance: No (standard)
- Details: Similar to RG-174, RG-178 cables typically use a PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) jacket, which offers some weather resistance but is not explicitly designed for UV protection. While PTFE is more durable than PVC, it is still not optimal for direct and prolonged outdoor exposure.

4. 0.81mm, 1.13mm, 1.32mm, 1.37mm Micro-Coaxial Cables
- UV Resistance: No
- Details: These micro-coaxial cables are often used for internal connections or applications requiring minimal size and weight. They are not designed with a UV-resistant outer jacket and typically have a PVC or thermoplastic outer layer. These cables are suitable for indoor use or short outdoor runs and are well-protected from sunlight, but they are not recommended for direct exposure to UV rays.

Summary Table
| Cable Type | UV Resistant | Outer Jacket Material | Recommendation for Outdoor Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| LMR-100 | Yes | Polyethylene (PE) | Suitable |
| LMR-200 | Yes | Polyethylene (PE) | Suitable |
| LMR-400 | Yes | Polyethylene (PE) | Suitable |
| RG-174 | No (standard) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Not recommended unless UV-rated |
| RG-178 | No (standard) | PTFE | Not recommended for direct exposure |
| 0.81mm | No | PVC or Thermoplastic | Not suitable |
| 1.13mm | No | PVC or Thermoplastic | Not suitable |
| 1.32mm | No | PVC or Thermoplastic | Not suitable |
| 1.37mm | No | PVC or Thermoplastic | Not suitable |
Recommendations for UV Protection
For outdoor installations:
- Choose LMR-series cables with polyethylene jackets for optimal UV resistance.
- Use protective conduit or UV-resistant sheathing if using non-UV-rated cables.
- Apply UV-resistant coatings or tape for additional protection on cables that must be exposed to sunlight.
UV-resistant cables like the LMR series provide a reliable solution for outdoor antenna installations, ensuring long-term performance and minimal maintenance.







