Antennas, Antenna Cables, Wireless Products: Technical Articles
Industrial IoT Platforms: Applications, Platforms, Benefits, Technologies
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) stands as one of the pillars of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, bridging the gap between the physical and digital realms of manufacturing. Central to this convergence is the IIoT platform—a software suite or solution that connects devices, analyzes data, and aids in decision-making. Let's delve into what Industrial IoT platforms are, their advantages, and their growing role in modern industries.
What are Industrial IoT Platforms?
Industrial IoT platforms are integrated software solutions that facilitate communication, data flow, and device management within industrial environments. Unlike consumer IoT platforms that focus on connecting smart homes and wearable devices, IIoT platforms are optimized for large-scale, rugged, and mission-critical operations.
Key components of Industrial IoT platforms include:
- Data Ingestion and Collection: IIoT platforms are equipped with data ingestion capabilities, allowing them to collect data from various sensors and devices deployed throughout an industrial environment. This data can encompass temperature readings, pressure levels, machine performance metrics, and much more.
- Data Analytics: Once the data is collected, Industrial IoT platforms use advanced analytics techniques, including machine learning and artificial intelligence, to derive valuable insights. These insights help industries make informed decisions, predict maintenance needs, and optimize operations.
- Device Management: IIoT platforms provide tools for managing and monitoring connected devices. This includes remote diagnostics, firmware updates, and device provisioning, ensuring that all connected assets are functioning optimally.
- Security and Compliance: Industrial IoT platforms prioritize the security of data and connected devices. They employ robust security measures such as encryption, authentication, and access controls to safeguard sensitive information and protect against cyber threats.
- Integration and Scalability: These platforms are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing systems and can scale to accommodate growing data volumes and device counts. This flexibility is crucial for industries looking to adopt IIoT incrementally.
- Visualization and Reporting: Industrial IoT platforms often include dashboarding and reporting tools that allow users to visualize data in real time. This makes it easier to track performance, monitor key metrics, and respond to anomalies promptly.
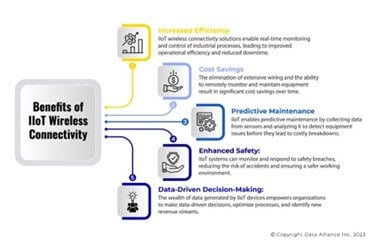
Benefits of Using IIoT Platforms
- Enhanced Efficiency: Real-time monitoring of machinery helps in proactive maintenance, reducing downtimes and ensuring optimal utilization of resources.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing patterns and anomalies, industries can predict when machinery is likely to fail, saving costs and time.
- Optimized Operations: Data-driven insights allow manufacturers to optimize their processes, leading to faster production and higher quality products.
- Energy Savings: Intelligent monitoring and management of energy-consuming devices lead to significant cost savings.
- Safety and Compliance: Real-time monitoring helps industries comply with safety regulations and standards, reducing risks of accidents.
Leading IIoT Platforms
As the IIoT ecosystem has evolved, several platforms have emerged as leaders in the sector:
- Siemens MindSphere: A cloud-based, open IoT operating system, MindSphere connects products, plants, systems, and machines.
- GE Predix: Designed for heavy industries, this platform offers tools for asset performance management and operations optimization.
- IBM Watson IoT: Watson offers powerful AI-driven analytics and is integrated with IBM's broader suite of enterprise solutions.
- PTC ThingWorx: This platform provides rapid application development, real-time analytics, and connectivity for industrial devices.
- Microsoft Azure IoT Suite: Leveraging Microsoft's extensive cloud infrastructure, Azure offers a wide range of tools for IIoT applications.
Applications of Industrial IoT Platforms
- Predictive Maintenance: IIoT platforms can predict when a machine will fail or requires maintenance. Sensors monitor equipment and send data to the platform where algorithms predict the likelihood of failure, enabling timely maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Supply Chain Management / Inventory Management: By integrating IIoT devices throughout the supply chain, industries can achieve real-time visibility, optimizing stock levels, reducing waste, and improving delivery timelines.
- Energy Management: Sensors can track energy consumption patterns, allowing industries to optimize energy use, identify wastage areas, and implement energy-saving measures.
- Quality Assurance: IIoT can continuously monitor manufacturing processes, ensuring that products meet the required standards and instantly flagging deviations.
- Safety and Health Monitoring: Wearable sensors can monitor workers' health metrics, environmental conditions, or detect the presence of harmful gases, ensuring a safe workspace.
- Smart Agriculture: Farmers can use IIoT for soil moisture monitoring, precision farming, livestock tracking, and optimizing irrigation systems.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Industries can remotely monitor operations, make real-time decisions, and implement changes from a central location, reducing the need for on-site interventions.
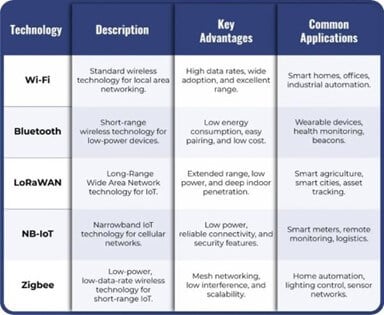
Top Wireless Technologies for IoT
| Technology | Description | Key Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi | Standard wireless technology for local area networking. | High data rates, wide adoption, and excellent range. | Smart homes, offices, industrial automation. |
| Bluetooth | Short-range wireless technology for low-power devices. | Low energy consumption, easy pairing, and low cost. | Beacons, monitors, network connectivity. |
| LoRaWAN | Long-Range Wide Area Network technology for IoT. | Extended range, low power, and deep indoor penetration. | Smart agriculture, smart cities, asset tracking. |
| NB-IoT | Narrowband IoT technology for cellular networks. | Low power, reliable connectivity, and security features. | Smart meters, remote monitoring, logistics. |
| Zigbee | Low-power, low-data-rate wireless technology for short-range IoT. | Mesh networking, low interference, and scalability. | Home automation, lighting control, sensor networks. |
Wireless Technologies Used in Industrial IoT Platforms (IIoT)
- Wi-Fi: A common choice for indoor applications due to its high data rate and direct integration with existing IT infrastructure.
- Bluetooth and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy): Ideal for short-range communications and situations where power consumption is a primary concern, such as with battery-operated sensors.
- Zigbee & Z-wave: Primarily used for home automation but also relevant for industrial applications, these are mesh network protocols which allow devices to communicate with each other without central coordination.
- LoRa (Long Range): It offers long-range connectivity with low power consumption, making it suitable for sensors that need to send small amounts of data over long distances.
- NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT): Designed for applications requiring wide coverage, long battery life, and a large number of devices. It's well-suited for remote monitoring.
- 5G: The latest generation of cellular networks, 5G offers high data rates, ultra-reliable low latency, and massive device connectivity, making it a promising option for industrial applications.
- RFID (Radio Frequency Identification): While not a communication technology in the traditional sense, RFID is vital for tracking inventory, assets, and products in real-time.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite the promise and potential, the IIoT journey isn't without challenges:
- Interoperability: With various devices from different manufacturers, ensuring seamless communication is a significant challenge.
- Data Privacy and Security: With increased connectivity comes the risk of cyber threats. Protecting sensitive industrial data is paramount.
- Skill Gap: The rapid evolution of IIoT requires a workforce skilled in both manufacturing and IT.
To tackle these challenges, industries are investing in R&D, training programs, and collaborating with tech giants and startups. As 5G technology becomes more prevalent, the bandwidth and speed it offers will further amplify the capabilities of IIoT platforms.







