Antennas, Antenna Cables, Wireless Products: Technical Articles
RP-SMA Connector Specifications, Applications, Key Characteristics, Composition
Table of Contents
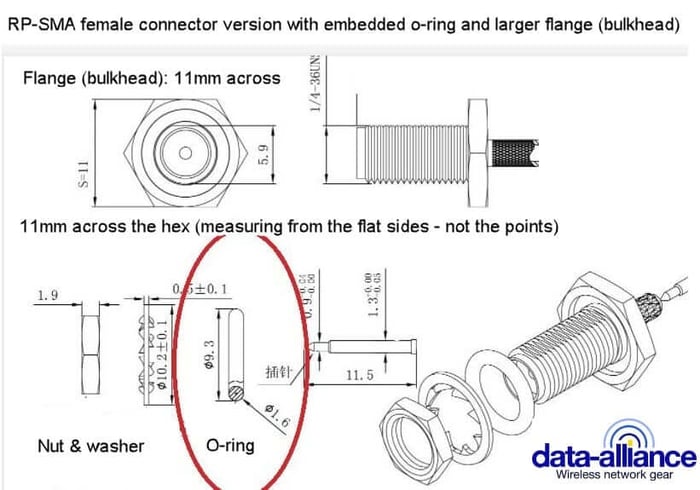
RP-SMA: Specifications and Key Characteristics
RP-SMA (Reverse Polarity SMA) connectors are widely used in wireless communications, particularly in WiFi, IoT, ISM-band, and RF antenna applications. Although mechanically similar to standard SMA connectors, RP-SMA connectors differ internally and are not directly interchangeable. Understanding the structure, gender definition, materials, and appropriate applications of RP-SMA connectors is essential for ensuring proper mating, minimizing signal loss, and maintaining long-term reliability in RF systems.
- RP-SMA is a variant of the SMA connector, called Reverse Polarity SMA. It is also known as SMA-RP, SMA-R. The only difference between RP-SMA and SMA is the orientation of the pin and socket, in the interior part of the connector (see photos). The reverse-polarity design was originally introduced to discourage the use of high-gain aftermarket antennas on consumer wireless equipment, particularly WiFi devices operating in unlicensed bands. Despite this intent, RP-SMA has since become a de facto standard connector type for many wireless products and accessories.
- RP-SMA gender is counter-intuitive: Please observe picture & note it is correct. The gender is referring to the pins inside--not the threads. RP-SMA male has threads on inside. More details regarding RP-SMA gender determination. This non-intuitive naming convention is one of the most common sources of confusion when selecting RP-SMA cables and antennas. Unlike many RF connectors where thread type determines gender, RP-SMA gender is defined solely by the center contact. Always visually inspect the connector or confirm specifications before ordering to avoid mismatched components.
- RP-SMA-male is also called "plug" and RP-SMA female connector is also called "jack."
- RP-SMA is a round screw-type connector, with medium-sized, threaded coupling connector that is rated for frequencies from the lowest (DC) up to 18GHz.
- RP-SMA connectors are not compatible with the common, commercially available Type F coaxial connector. Type F connectors look similar but are of slightly different size and will not pair with RP-SMA connectors without an adapter. Although RP-SMA and SMA connectors share the same outer thread dimensions, they are not electrically compatible. An RP-SMA male will mechanically thread onto an SMA female, but the center contacts will not mate correctly. This can result in an open circuit, intermittent connection, or physical damage to the connector. Adapters should only be used when explicitly designed for SMA-to-RP-SMA conversion.
Typical electrical and mechanical specifications of RP-SMA connectors include:
Characteristic
Impedance: 50 ohms
Frequency range: DC to 18 GHz (depending on cable and connector quality)
VSWR: Typically ≤ 1.3:1 at lower GHz ranges
Mating cycles: Typically 500 cycles minimum
Coupling mechanism: Threaded (1/4-36 UNS)
Environmental rating: Indoor or outdoor depending on plating and sealing
These specifications make RP-SMA connectors suitable for a wide range of RF and microwave applications where compact size and moderate frequency performance are required.
Materials Composition of RP-SMA-male Connectors
- Connector Body:
- Connectors for indoor use have a gold-plated brass body (in almost all cases), because this is the best alloy for the connector-body (unless intended for outdoor use).
- Connectors for outdoor use that are expected to be exposed to water or weather have a nickel-plated brass body, which is the best protection from corrosion and rust. RP-SMA adapters for outdoor use are always made with nickel-plated brass.
- In summary: Most RP-SMA connectors for antenna cables have a gold-plated brass body, and in cases in which the RP-SMA cables or RP-SMA antennas are intended for outdoor use, we can make them with a nickel-plated brass body for corrosion protection.
- Brass is widely used due to its excellent balance of electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and machinability. Gold plating is preferred for indoor applications because it minimizes contact resistance and oxidation, while nickel plating is favored outdoors due to its superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
- Center Contact:
- Beryllium Copper, Gold Plated. Gold is a highly effective conductor and is resistant to corrosion. The gold plating ensures low signal loss with a consistently high-quality connection, even with frequent mating and de-mating cycles over time.
- Beryllium copper is selected for its excellent spring properties, which ensure consistent contact pressure over repeated mating cycles. This contributes to stable impedance and low insertion loss throughout the lifetime of the connector.
- Crimp Ferrule:
- Nickel Plated Copper
- The crimp ferrule provides a secure mechanical bond between the connector and coaxial cable shield. Proper crimping is essential to maintain shielding effectiveness and prevent signal leakage or impedance discontinuities.
- Insulators:
- PTFE, which insolates the central conductor from the outer shielding, preventing short-circuits and interference. PTFE has high resistance to heat and is an excellent insulator.
- PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) is used due to its low dielectric constant, low loss tangent, and high thermal stability. These properties are critical for maintaining signal integrity at higher frequencies.
Common applications of RP-SMA connectors
RP-SMA connectors are commonly used in:
• WiFi routers and access points
• Wireless LAN antennas
• IoT and M2M devices
• ISM-band radios (900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz)
• Embedded wireless modules
• Test and measurement setups
• RF extension cables and adapters
Their compact size and threaded coupling make them especially suitable for devices where vibration resistance and secure connections are required.
RP-SMA connectors are typically terminated on low-loss coaxial cables such as RG-174, RG-316, RG-58, LMR-100, LMR-195, and LMR-240. The choice of cable impacts overall system loss, flexibility, and environmental durability. Connector performance should always be evaluated in combination with the selected cable type.
Installation and handling considerations
RP-SMA connectors should be tightened using the correct torque to avoid damage. Over-tightening can deform the dielectric or center contact, while under-tightening can lead to poor electrical contact. Using a dedicated RP-SMA wrench helps ensure consistent and repeatable installations.
Care should also be taken to avoid cross-threading, especially when mating RP-SMA connectors with adapters or bulkhead fittings.
Summary
RP-SMA connectors remain a cornerstone of modern wireless connectivity, offering reliable performance across a broad frequency range when properly specified and installed. While their reverse-polarity design can be confusing, a clear understanding of connector gender, materials, compatibility, and application requirements ensures optimal RF performance. When paired with appropriate coaxial cable and installed using best practices, RP-SMA connectors provide durable, low-loss connections for a wide variety of wireless systems.
FOOTNOTES:
- We offer an RP-SMA wrench to assist in installing antennas, cables and adapters with RP-SMA or SMA connector(s).
- Data Alliance's RP-SMA connectors are precision machined for low loss in ISO 9001 facilities.
- Proper connector selection, correct gender identification, and high-quality materials are critical factors in minimizing insertion loss, return loss, and long-term degradation in RF systems.
RP-SMA Connectors:
FAQs
What is an RP-SMA connector and how does it differ from SMA?
RP-SMA (Reverse Polarity SMA) is a variant of the standard SMA connector in which the center pin and socket are reversed. While the outer threads and mechanical dimensions are the same, the internal center contact is different, making RP-SMA and SMA connectors electrically incompatible without a proper adapter.
How is RP-SMA connector gender determined?
RP-SMA gender is determined solely by the center contact, not by the threads. An RP-SMA male connector has internal threads and a center socket, while an RP-SMA female connector has external threads and a center pin. This counter-intuitive definition is a common source of confusion, so visual inspection is recommended before ordering.
Are RP-SMA and SMA connectors interchangeable?
No. Although RP-SMA and SMA connectors share the same thread size and will mechanically mate, their center contacts do not align correctly. This can result in signal loss, intermittent connections, or physical damage. Only adapters specifically designed for SMA-to-RP-SMA conversion should be used.
What frequency range do RP-SMA connectors support?
RP-SMA connectors are typically rated for frequencies from DC up to 18 GHz, depending on connector construction, materials, and the coaxial cable used. When properly installed, they provide stable impedance and low VSWR across common RF and microwave bands.
What materials are used in RP-SMA connectors and why?
RP-SMA connectors typically use a brass body with gold plating for indoor applications or nickel plating for outdoor corrosion resistance. The center contact is made from gold-plated beryllium copper for consistent contact pressure and low loss. PTFE insulation is used due to its excellent dielectric properties and thermal stability.
What are common applications for RP-SMA connectors?
RP-SMA connectors are widely used in WiFi routers, wireless LAN antennas, IoT and M2M devices, ISM-band radios, embedded wireless modules, and RF test equipment. Their threaded coupling provides a secure, vibration-resistant connection suitable for both consumer and industrial wireless systems.








